Did you know only 60% of small trials can find the best low dose for an effective drug? This fact shows a big problem in how we give medicine. Finding the right dose and timing is key. It helps patients get the most from their treatment and stick to it. This guide looks closely at how different dose schedules affect how well drugs work. It aims to help health pros manage patients better.
Nowadays, drug dosing is changing due to real-world data and new prediction methods. The FDA wants drug dose studies early in the review process. This checks that drugs are safe and work well for all kinds of patients. These steps are important to make sure medicines help everyone, including babies and older people. Learn more about Dosage and Timing for Optimal.
Key Takeaways
- Determining the optimal dosage can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
- Timing in medication administration is critical for maximizing the effectiveness of drug regimens.
- Real-world data and predictive models are increasingly vital in dosage decision-making.
- Regulatory guidance underscores the need for dose optimization comparisons in initial drug studies.
- Patient education is essential for improving adherence to prescribed medication.
Introduction to Dosage Optimization
Dosage optimization is key for effective medication use. It means changing a drug’s amount for each patient. This ensures the best results and the least side effects. Factors like age, weight, and health conditions matter in this process.
Studies show that drug doses often need changes after they hit the market. From 1980 to 1999, about 20% of new drugs had their doses adjusted. It’s vital, especially for drugs with different starting and maintenance doses. Drugs for the brain and immune system often need big dose cuts.
Dose adjustments are not just for new drugs but for all medications. Checking kidney and liver health is important before and during treatment. People like the elderly, children, and those who had bariatric surgery need special dose considerations. Making these adjustments can improve health outcomes, showing the value of personalized dosing.
The Importance of Timing in Medication Administration
Timing is key when you take medicine. Studies show giving medicine at certain times can really help. For example, 40% of drugs work best taken with food. This tells us when to take them for the best effect.
Sticking to your medicine schedule is crucial, especially for long-term illness. Only half of those with chronic diseases keep up with their meds. Doctors stress timing to help patients stick with their plans. Medication timing, or chronotherapy, is becoming more known, especially for illnesses like asthma.
Some antibiotics need to be taken at set times to work right. Antidepressants have specific times too, based on their effects. Some are for night, others for morning.
NSAIDs, like ibuprofen, should be taken with food. This helps avoid stomach issues. These details show how complex and vital proper medicine use is.
Pill organizers can help people take their medicine correctly. This is important since over 20% of adults over 40 use five or more medicines. Being organized helps a lot.
Keeping medicine in the right place is as important as taking it on time. Doing a medicine check-up each year is a good idea. This helps keep treatment up to date. For more on timely medicine taking, learn more here.
| Medication Category | Timing Recommendation | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Evenly spaced during waking hours | Maintains effective concentration |
| NSAIDs | With food | Reduces gastrointestinal adverse effects |
| Antidepressants | Bedtime or morning depending on sedative potential | Minimizes next-day drowsiness |
| Corticosteroids | Timed with circadian rhythms | Enhances effectiveness for certain conditions |
Understanding Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics plays a key role in setting the right medication dosages and timing for treatment. It explores how the body handles drugs, focusing on absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Knowing this process allows healthcare providers to prescribe medicines more effectively, boosting medication effectiveness.
Impact of Absorption Rates
The speed at which a body absorbs a drug can greatly impact its effectiveness. Absorption rates vary due to factors like the drug’s make-up, how it’s given, and individual body differences. For instance, pills work differently from injections. By enhancing absorption, drugs can work better and satisfy patients more.
Distribution within the Body
After a drug is absorbed, it moves through the body. The drug distribution process depends on various factors including how it spreads and binds to proteins. High distribution medicines may work fast but might also have greater side effect risks. Knowing drug distribution helps experts create personalized dosing plans for the best effect. For more about pharmacokinetics, check out this resource.
Therapeutic Window: Finding the Right Dose
The idea of the therapeutic window is key when giving meds. This window shows the doses that are both effective and safe. Finding the right dose within this window helps patients get better without bad side effects.
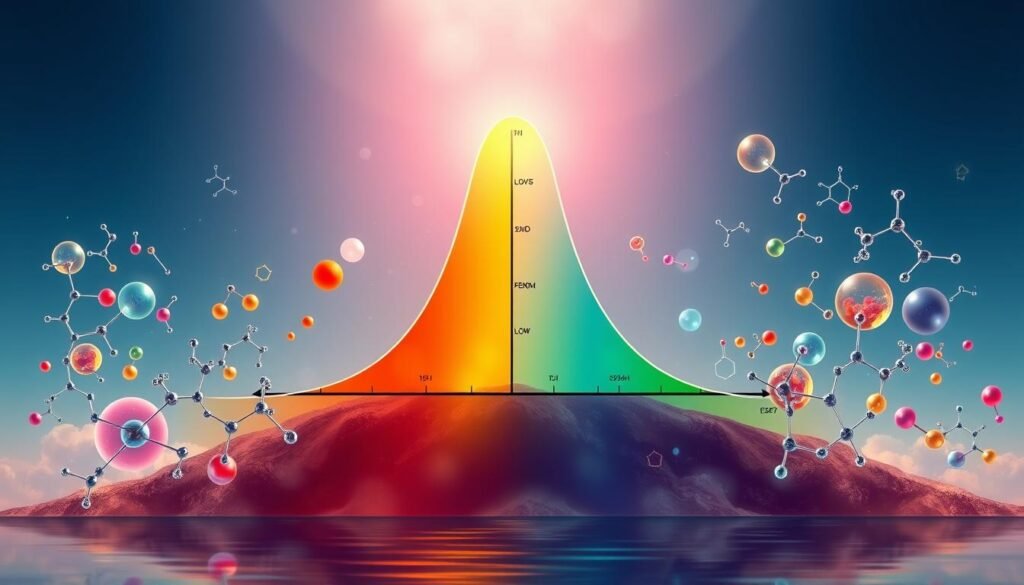
Healthcare pros use different ways to find this window. One common method is therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). TDM is used for drugs like lithium and warfarin. It measures drug levels in the blood to keep the dosage just right.
Knowing the therapeutic index (TI) helps understand a drug’s safety. The TI compares the harmful dose to the effective dose. For example, remifentanil has a wide safety margin. But, digoxin has a TI showing a higher risk, which means it needs careful monitoring.
| Drug | Therapeutic Index | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Remifentanil | 33,000:1 | Broad safety |
| Digoxin | 2:1 | Narrow safety |
| Warfarin | 10:1 | Narrow safety |
| Lithium | 10-20:1 | Narrow safety |
Precision dosing is a new way to make treatments better. It adjusts doses for each patient’s unique situation. This method is promising for safer, more effective care. Tailoring doses is becoming crucial as healthcare shifts towards value-based care.
Dosage and Timing for Optimal Effectiveness
Getting the dosage timing right is crucial to get the most out of exercise medication. When you time it right, the body reacts better to meds and supplements. It is often advised to take some meds before or after working out. This can boost their effects and your performance.
Pre-Exercise vs. Post-Exercise Timing
It’s key to understand the effects of timing on meds like caffeine or protein shakes. For example, caffeine before exercising can increase stamina and focus. On the flip side, protein after a workout helps with muscle healing and growth. This shows why individualized dosing strategies that match your goals and health needs matter a lot.

Individualized Dosing Strategies
Making a med plan that’s just for you is key to getting the best results and sticking with it. This method looks at your age, weight, and health issues to tailor your dosage and timing. For instance, changing based on how often and hard you exercise can lead to better health. Check out this link for more on following your med schedule closely.
This approach doesn’t just make meds more effective. It also makes patients happier and more likely to stick with their plans. By giving meds at the best times, doctors can greatly improve how well these meds work.
Acute vs. Chronic Administration of Medications
It’s key to know the difference between acute and chronic medications for good treatment results. Acute medications are for short-term, focusing on current symptoms. Chronic medications, in contrast, are used regularly for a long time to manage continuous health issues. Knowing these differences helps make treatment better and keeps patients on track.
Short-Term Use Considerations
For acute medications, how and when you take them is really important. For instance, topiramate can quickly lower alcohol use. Studies show that taking medicine for a short time can manage conditions like alcohol use disorders effectively. Mixing ondansetron with topiramate seems hopeful. Using these medicines for a short period helps decrease symptoms and prevents treatment resistance.
Long-Term Treatment Adherence Strategies
Sticking to chronic medications is vital for their success. But patients often find it hard to keep up due to complicated schedules or not knowing how the medicine helps. For long-term treatments, like with topiramate, supporting patients to stay consistent is essential. Doctors should use proven methods to stress the importance of regular medication use. They should also follow up often and teach patients about the benefits and side effects of their medications. Knowing the pros and cons is crucial for those on chronic medications.
Side Effect Management Through Proper Timing
Managing side effects is key to improving patients’ experiences during treatment. It helps them stick with their therapy plans. By planning when to take medicine, patients can lessen bad reactions. This planning often involves their meal times and when they sleep.
Identifying and Mitigating Risks
Healthcare workers need to spot risks with medicines. For example, many taking SSRIs face unwanted reactions. About 86% of these patients reported side effects within three months. Of these, 55% thought the side effects were hard to handle.
It’s important to notice how different groups, like kids and seniors, may respond. Each group can react in its own way to the same treatment.
Patient Education and Compliance
Telling patients about their medicines makes them more likely to follow the plan. This is because over 33% stop taking antidepressants due to bad reactions. Good communication about possible side effects is crucial. It helps patients feel prepared.
Healthcare providers must talk about when it’s best to take each medicine. This can help avoid quitting the treatment. It also helps get the best results from the medicine.
Role of Medication Scheduling in Treatment Adherence
Medication schedules are key for sticking to treatments. Research found that a set medicine timetable improves how well patients follow their regimen. A deep dive into articles from 1998 to 2007 looked at what affects adherence, zeroing in on 61 studies. These studies showed how often you take your meds matters a lot for sticking to the plan.
Looking through 76 studies with electronic tracking, patients hit a 71% success rate in taking medicine across different sicknesses. Folks taking pills once a day stuck to their schedule better than those taking them three times a day. But once-daily and twice-daily routines didn’t really show a difference in success. Reducing the number of doses a day not only made people more likely to take their medicine, but it also showed that taking medicine once or twice a day was better than three times.
When doctors make medicine plans simpler, patients are more likely to follow through. Pills that last longer and have fewer side effects are great for once-a-day schedules. Not following the plan can vary a lot, from as little as 10% to as much as 92%. On average, about 50% of people in wealthy countries stick to their medicine plans. Half the time, people don’t follow their regimen on purpose, the other half because it’s complex or they don’t understand it.
About 50% of people with long-term diseases take their meds like they’re supposed to. But those with short-term sicknesses do a bit better. For older patients, adherence is between 38% and 57%. Also, 40% to 60% of patients might not get their doctor’s directions right after a visit.
When treatment aims to cure a disease, 77% of patients do well in following it. This drops to 50% for treatments meant to prevent health issues over time. If patients don’t feel sick, they’re less likely to stick to their medicine. Factors like gender, personality, and culture can also play a role, with women often doing better, especially with meds for mental health.
To help patients keep up with their meds, doctors should make them part of the decision process. Simplifying complex medicine schedules also helps a lot in improving how well treatments work.
| Frequency of Dosing | Average Compliance Rate | Patient Group |
|---|---|---|
| Once Daily | ~71% | General Population |
| Twice Daily | No significant difference | General Population |
| Thrice Daily | ~50% | Chronic Condition Patients |
| Elderly Patients | 38% – 57% | Elderly Population |
Conclusion
The success of your medication depends on the right dosage and timing. This guide has shown why both are crucial for staying healthy. When you think about how much and when to take your meds, you can avoid side effects and get better results.
Learning all you can about your meds is key. When you know the effects of your medicine and how timing matters, you take control of your health. This knowledge helps you stick to your treatment and get healthier.
Understanding how to manage your medication means you can enjoy better health. Armed with the right information, you can handle your medical care with more confidence. This leads to a faster recovery and a stronger, healthier you.